It has become increasingly difficult for businesses to compete in the international markets in the modern globalized era. To have an edge and be competitive, companies need to be constantly dishing out innovations that their customers will appreciate. Being innovative and remaining on top of your competition is not an easy task, but living labs can significantly help. This article will explain the concept of living labs and how living labs contribute to innovation, focusing on the agricultural sector.
What are the Living Labs?
As there is growing consumer demand for product innovations, there is a shift from a product-based economy to a user-centred one. Putting the user as the main focal point means that product innovations are suited to the end user’s needs based on an active feedback process, what we call a living lab. The concept of living labs can be explained as a user-driven collaborative environment that drives innovation and helps deal with safety, quality, and sustainability challenges.
How can Living Labs be used in the Agricultural Sector?
Having explained how living labs contribute to innovation, we want to highlight the advantages of living labs to agriculture. As agriculture is one of the main sectors in rural areas, it is even more crucial to support innovation in agriculture. With the observed ongoing rural areas depopulation, the timing is critical to achieving sustainable economic and social development for rural areas that will make them attractive and create local entrepreneurial opportunities.
Most importantly, through the living labs dynamics, they can boost partnership creation, new business development and synergies exploitation. These are some very crucial aspects in rural areas as they remain underdeveloped. Rural living labs can formulate new partnerships and engage multiple stakeholders and policymakers to bring much-needed innovations in the agricultural sector. A rural living lab can hasten infrastructure investments such as ICT-based innovations specifically tailored to agriculture like crops monitoring, new business models and value capturing approaches.
The Case of LIVERUR Living Lab
LIVERUR is a European Horizon 2020 project that introduced the Rural Living Lab research methodology to Small – Medium – Agricultural Enterprises (SMAEs). LIVERUR, with the use of Rural Living Labs, contribute to innovation with the development of the RAIN platform and tools to help living labs users develop their projects.
The novelty of LIVERUR is the design of an innovative business model, based on the RAIN concept, for rural areas to move towards a circular economy, open innovation, information, and communication focus. The RAIN concept is characterized by the:
- Rain core Elements
- Rain Principles
- Rain Real-Life Setting
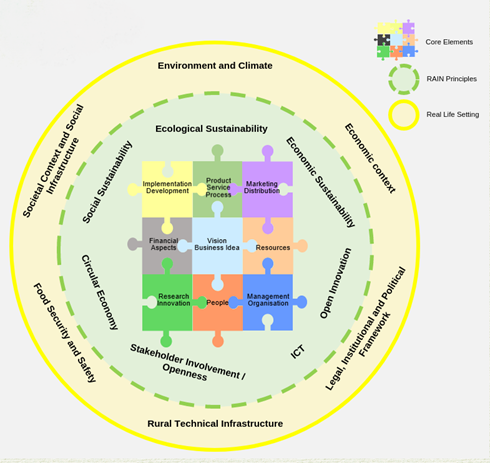
LIVERUR Rural Living Labs are based on the following premises:
- Building Local User Communities according to LIVERUR’s main goals
- User Involvement
- Strategic partnership building stakeholders
- Partners that are users or citizens involved with innovations
- Phasing, cyclic, and spiral development
- Networks and synergies were created by developing open-source licenses for tools and services for local developers and entrepreneurs.
Conclusion
The sustainable development of rural areas is crucial to avoid depopulating those areas and safeguard the production of sustainable and safe agricultural products. The introduction of Rural Living Labs to agricultural regions will provide a new breath of hope for local entrepreneurs; it will halt depopulation and, hopefully, make a living in rural areas to be on par with urban environments. The contribution of LIVERUR Project and the living labs to innovation in the agricultural sector will significantly impact sustainable rural development.
To learn more about LIVERUR European project, you can visit the official website.

