I don’t think there was anyone who could even fathom the extent of the pandemic’s impact on the economy. But NGOs and civil society organizations were most affected, especially those dealing with youth. This was due to the nature of their operations, which involved a lot of in-person training, but also their small size.
This article will show you the findings of the “Europe-wide NGO Pandemic Impact Survey Report” we have just released with our partners.
It contains the answers of 374 NGOs active in different areas and coming from 46 countries around Europe. Except for the pandemic impact on NGOs, this report also mentions the best practices these organizations employed to deal with their challenges. The last part is really useful as it can give ideas to NGOs on how to deal with similar adverse situations in the future.
Let’s find out.
What are the findings of the pandemic impact on NGOs?
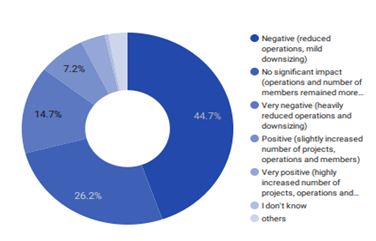
86% of NGOs reported a negative or no impact
This is not a surprising result. Specifically, 45.1% of NGOs said the impact was negative, leading to reduced operations and a mild downsizing. 26.2% of the respondents said that COVID-19 had no impact at all on their activities. A 14.8% said that their organization was heavily impacted by a severe reduction in their operations and the number of staff.
Interestingly, 6.8% declared a positive impact, and 3.6% an extremely positive impact with a subsequent increase in new projects, operations, and staff.
The pandemic impact was higher in smaller organizations
Small businesses were the most likely to report and suffer negative consequences from the pandemic, with reduced number of operations and moderate downsizing. On the other hand, medium and large organizations seem to have been less affected. The conclusion is that large organizations have higher chances of adapting to the new context, while smaller ones are more vulnerable to these changes.
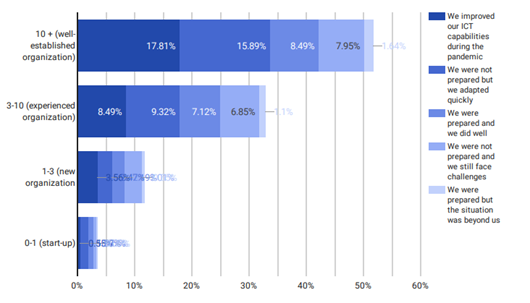
Older organizations were able to make more effective changes
To deal with the new situation of the pandemic ICT skills played a really important role. Our findings showed that the older an organization was, the more effective they were in improving their ICT skills and online tools. Smaller organizations were totally unprepared but had to adapt rapidly to survive in the new climate.
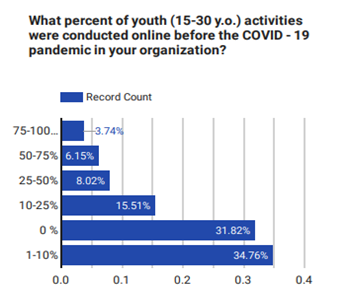
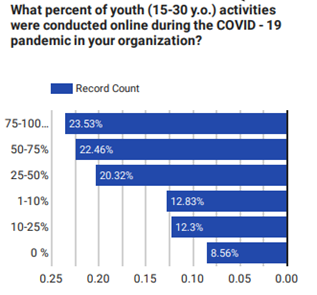
Youth activities became overwhelmingly online
Before the impact of the pandemic, most youth activities were happening on-site and in-person as it was more effective and there were no health concerns. However, as soon as NGOs started to feel the pandemic impact and realized that this was not viable anymore, going online seemed the only viable option. That’s why improving their ICT, and digital skills were important, as we saw above. The chart that follows shows the changes that occurred during the pandemic.
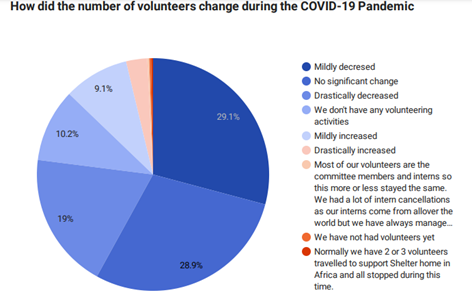
The number of volunteers decreased
With all the restrictions in place and since most activities moved online, the number of volunteers was reduced as expected. 29.1% of NGOs reported that they saw a mild decrease in their volunteers during the pandemic, while 19% saw a drastic decrease in their volunteers. 28.9% saw no notable change in the number of volunteers. On the other hand, 9% of organizations benefitted from the pandemic impact with a mild increase in their volunteers, and 2.7 % saw a drastic increase.
Not all NGOs received external support to cope with the pandemic
The pandemic was stressful for both organizations and individuals as they saw their revenues plunge, but their costs remained the same. For this reason, it was necessary for Governments to provide support or some kind of relief to financially struggling businesses or NGOs.
In our report, we found that despite the adverse pandemic impact, not all NGOs had access to this kind of help. 46.8% of NGOs responded that they received no help at all, 12.3% received help from their National Governments, 9.9% received aid from their local government, 9.9% received support from international funds (EU, UN, UNICEF), 8.8% got donations and sponsorships, 5.5% were assisted by other NGOs, and 7% benefited from other types of support.
NGOs needed technical infrastructure and cooperation
The transition to online activities created the need for hardware, software, and technical support to realize the digital transition and combat the pandemic impact. The online platforms that were widely used to facilitate the volunteering activities also required, in many instances, the modernization of work and IT equipment. NGOs also sought increased cooperation with NGOs and other organizations, institutions, and agencies since they faced common challenges. With collaboration and partnerships, they could identify their immediate needs and share best practices that provided solutions to their problems.
The best practices to deal with the pandemic impact on NGOs
Two years into the pandemic, the impact is not as high as it used to be since organizations have adapted their activities to the new reality. To make this report as valuable as possible to NGOs, we gathered their best practices that helped them overcome the obstacles of the pandemic. Their responses were grouped into six areas of solutions and best practices:
- The framework of online youth volunteering
- Motivation, participation, and engagement
- Digital support and literacy
- Training and learning priorities
- Innovation and cooperation
1. Create a framework for online volunteering
The experts who responded to the survey suggested a robust framework for online volunteering to provide youth with the experience possible adapted to the new reality. This should involve a Code of Conduct with instructions on recurring activities to make the onboarding process easier and allow them more autonomous work.
NGOs should maximize their outreach by using high-quality online portals that could help them with recruitment and information dissemination. In light of the transition to the digital era, this framework should involve local, national and European institutions to facilitate online volunteering actions.
2. Keep the motivation and participation of youth at high levels
This idea is central to volunteering activities as volunteers must have the best experience to feel it was worth their time. NGOs should strive to create non-passive experiences and to empower their volunteers by being proactive. Additionally, volunteers must have their own voice in the organization. Encouraging their initiatives would help. That’s how NGOs can manage the active participation of their volunteers, make them “co-builders”, and keep them motivated.
3. Maintain high digital support and literacy
Since we are talking about e-volunteering, organizations must ensure that their volunteers have access to proper infrastructure, the digital skills needed, and access to information. NGOs should be proactive in getting the best digital tools necessary for a successful online implementation.
4. Prioritize volunteer training
The new digital landscape requires digital skills that not everyone has. Therefore, NGOs should determine the digital literacy levels of their volunteers and train them. This is not only about upskilling them but also connecting with others. Volunteers must be properly trained and equipped to deal with any situation, like a pandemic. NGOs should be the ones to provide this assistance to empower their volunteers so that they can continue working in civil society.
5. Increase cooperation
Digital volunteering can benefit from close monitoring, collaborations, and partnerships with grassroots organizations. NGO cooperation can create better guidelines, identify shortcomings, and develop new solutions. It can also help create better marketing strategies at national and international like creating an online portal for small NGOs to increase their visibility. Finally, cooperation between volunteering NGOs can raise awareness of the benefits of digital volunteering and eliminate the prejudices that exist.
The report was a result of the E-Volunteering project

The report on the pandemic impact on NGOs was produced in collaboration with our partners in the E-Volunteering Erasmus+ project. This project started during the pandemic in 2021, when restrictions were in full effect.
This situation was tough for young people since they had little to no opportunities to increase their skills and professional experience. But that was not the only challenge for youth and youth organizations since everything had to become digital. This created additional problems for both lacking the digital skills and infrastructure to deal with this new situation.
This project is important to record all the best practices implemented by European organizations during the lockdown to keep their volunteers active and continuously motivated. Additionally, the project will keep track of the IT tools used for communication and training purposes. Later on, it will also develop its own tool to help volunteers and organizations find each the meet their needs and expectations. Finally, as the name suggests, together with our partners, we will promote e-volunteering to increase their skills and competencies.
How did you find our report? We hope that you found it as valuable as we did.
Read the full report on the “Europe-wide NGO Pandemic Impact Survey Report” here.
If you are interested in discussing collaboration opportunities on EU programmes in volunteering or any other relevant field, do not hesitate to contact us to be our partner.

![How Has Covid Affected NGOs During the Pandemic? [+Best Practices]](https://ied.eu/wp-content/uploads/2022/08/impact-pandemic-ngos.jpg)